Computing
Vision
At Fair Field, our vision is for every child to receive a relevant, inspiring, and future-ready computing education. We aim to ignite curiosity, foster creativity, and equip children with the knowledge and skills they need to navigate and contribute to an ever-evolving digital world.
We believe Computing should empower pupils to become responsible digital citizens, confident creators, and critical thinkers. Through a carefully sequenced curriculum, pupils build a deep understanding of technology’s role in their lives and futures.
By the time pupils leave Fair Field, they will have developed the fluency, confidence, and integrity needed to use technology creatively, safely, and effectively—ready to thrive in secondary education and beyond in our increasingly digital world.
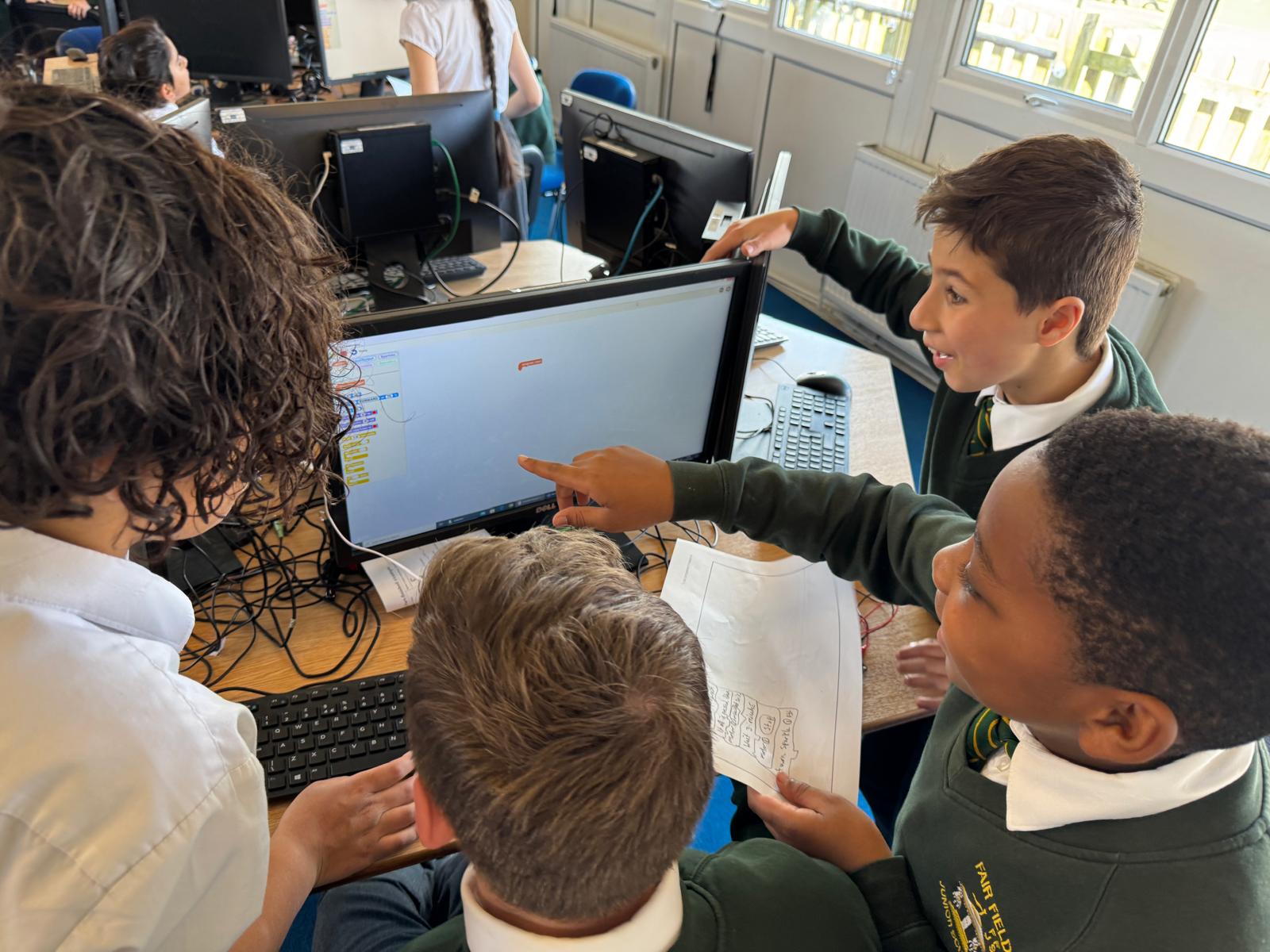

How we teach Computing at Fair Field
We follow the Teach Computing Scheme, which provides a clear progression across Key Stage 2 and is structured around six key strands that revisit and build knowledge each year. These strands ensure pupils develop a strong foundation in computing knowledge and practical application.
Our Computing curriculum is built around the following six strands:
1. Computing Systems and Networks
Pupils explore how digital systems and networks function—from learning what a computer is, to understanding the internet, data transfer, and how systems work together. They gain a real-world understanding of how digital technology operates in everyday life.
2. Creating Media (A)
In this strand, pupils use digital tools to create content such as posters, videos, animations, and presentations. They learn to evaluate, refine, and communicate information effectively through media while developing key editing and design skills.
3. Programming A
Pupils begin to understand algorithms, sequence, repetition, and selection. They create and debug simple programs using block-based coding and progress toward applying logic and predicting outcomes in increasingly complex tasks.
4. Data and Information
This strand teaches pupils how to collect, organise, and analyse data. They learn to use tools such as spreadsheets, databases, and charts to draw conclusions and solve problems, linking digital skills to real-life application.
5. Creating Media (B)
A second strand of media creation that builds on earlier units, this includes more complex projects such as website design, video editing, or digital storytelling—giving pupils greater autonomy and creativity in their use of digital tools.
6. Programming B
This more advanced programming strand revisits and deepens understanding of logic, inputs, outputs, and variable use. Pupils plan, write, and test more structured programs, developing resilience and computational thinking.
o enhance our offer, we also make purposeful use of digital platforms such as Times Tables Rock Stars (TTRS) to build fluency in maths and SATs Boot Camp to support revision and digital literacy skills. These tools help children develop confidence in using technology to practise, retrieve, and apply knowledge across subjects.
Online Safety is woven throughout the curriculum and addressed explicitly in every year group. Pupils learn to identify risks, act responsibly online, and seek help when needed. This work is supported by themed assemblies, dedicated lessons, and wider curriculum links to PSHE.
By revisiting these strands regularly, building knowledge year on year, and applying digital skills in real-world contexts, our pupils become fluent, capable, and reflective digital citizens—well-prepared for the demands of the digital world ahead.
